Dispersers and Immersion Mills
The Next Generation of Rotor Stators: Innovation in Wet Grinding and Dispersion Technology
Rotor stators have long been a cornerstone of wet grinding and dispersion processes, offering effective solutions for breaking down agglomerates and creating stable emulsions. With technological advancements, Hockmeyer Equipment Corporation has redefined rotor stator performance, delivering unparalleled efficiency, precision, and versatility. In this article, we explore the next generation of rotor stators, their principles, and how they can optimize your production processes.
Understanding Rotor Stator Technology
At its core, rotor stator technology uses high-speed shearing forces to break down particles and emulsify materials. The rotor, a high-speed spinning blade, works in conjunction with the stator, a stationary element with precisely engineered slots or holes. Together, they generate intense turbulence and shear, effectively reducing particle size and blending ingredients.
Traditional rotor stators have been used in two primary configurations:
- Drop-In Rotor Stators: Inserted into the top of a mix tank, these units are lowered and raised as needed for batch processing.
- In-Line Rotor Stators: These systems process materials in a continuous flow, moving them to a holding or recirculation tank for further refinement.
While effective, these systems have inherent limitations related to slot size, rotor speed, and heat generation. Hockmeyer’s next-generation designs address these challenges head-on.
Innovations in Rotor Stator Design
Hockmeyer’s innovative rotor stator systems incorporate state-of-the-art features to enhance performance and overcome traditional obstacles. Key advancements include:
- Variable Slot Stator Technology: The patented design allows for rapid initial size reduction of large agglomerates, which are then progressively refined through smaller slots. This staged process ensures a uniform dispersion and maximized surface area for chemical reactions.
- Temperature Control: High-shear devices often generate heat during operation, which can be problematic for heat-sensitive materials. Hockmeyer’s HRX Series rotor stators feature temperature-regulated jackets on the surrounding dome, maintaining optimal processing conditions.
- Integrated Vacuum Capabilities: Air entrainment is a common issue in dispersion processes, leading to foam formation and lower-quality product. The NexGen vacuum rotor stator operates under a self-generated vacuum, eliminating air bubbles and ensuring a smooth, homogeneous dispersion.
Optimizing Processes for Different Applications
Rotor stator technology can be tailored to meet a wide range of application needs. Here are a few examples:
- Rubber Crumbs in Solvent: Large rubber chunks, up to 1 inch in size, are rapidly reduced using a saw tooth disperser blade. The variable slot stator then refines these pieces into smaller fragments, exposing maximum surface area to the solvent for efficient dissolution.
- High-Viscosity Formulations: For applications involving high-viscosity slurries, additional tools like low-speed sweeper blades or augers can be integrated. These components help feed the rotor stator effectively, maintaining consistent throughput.
- Air-Sensitive Processes: The NexGen vacuum rotor stator ensures air-free dispersions while recirculating materials at high speeds, delivering exceptional results for both small and large batches.
Enhancing Efficiency and Profitability
Hockmeyer’s next-generation rotor stators deliver measurable improvements in efficiency, productivity, and cost savings. Benefits include:
- Higher Throughput: Faster processing times mean more product in less time.
- Reduced Waste: Precise control over dispersion minimizes raw material loss.
- Streamlined Cleanup: Innovative designs simplify maintenance and cleanup, reducing downtime.
Moreover, these machines are equipped with remote processing controls, allowing operators to monitor and adjust parameters in real time for consistent, repeatable results.
Partnering With Hockmeyer for Custom Solutions
Relying on over 80 years of expertise in wet grinding and dispersion technologies, Hockmeyer’s team of engineers and applications specialists works closely with clients to develop customized solutions. Whether your goals involve increasing capacity, reducing production costs, or improving product quality, we have the knowledge and experience to make your project a success.
Learn More
Explore the full potential of rotor stator technology with Hockmeyer Equipment Corporation. Visit our comprehensive guide, The Rotor Stator Principles Guide: Everything You Need to Know, for detailed insights and discover how our cutting-edge machines can transform your production processes. Ready to take the next step? Contact us today to discuss your application needs.
Nano Range dispersions
Nano range dispersions have been successfully achieved on media mills using extremely small media, in some cases, down to .03 mm diameter. This is expensive from a media cost and screening cost perspective. It is also quite time-consuming, sometimes hundreds of media milling hours as the particle size approaches and enters the single digit nanometer range. This is normally accomplished through the arduous process of pre-dispersing on a high-speed disperser or a rotor stator and then moving on to the smallest size media capable of bringing the feedstock into the nanometer range.
The objectives of time and cost reduction can be achieved more rapidly if the number of incremental steps can be reduced.
As particles (agglomerates) are reduced in size, surface area increases causing an increase in viscosity. This increases vehicle demand and, if not satisfied, will inhibit further dispersion. Manufacturers of certain types of coatings such as inks find higher solids loadings (30%) desirable. However, reaching the single digit nano particle range precludes the higher solids loading. The media loses its dispersion ability as it succumbs to the high cumulative mass resistance to its’ shear and impact. To reach the low nanometer range the dispersion must be almost water-thin (500-1000 cps).
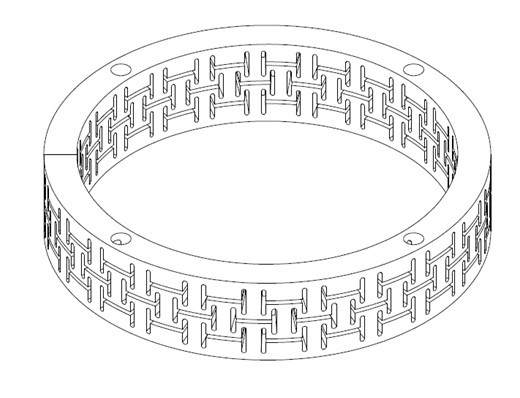
Reverting back to step reduction, the first: pre-dispersion, can be done in a rotor stator using the smallest slots practical (1mm) in a configuration offering the greatest combined amount of open area, interlocking “H” shaped slots. The process requires a measured rate of solids introduction through an in-line powder feed incorporating a downstream educator positioned between the feed cone and the NexGen rotor stator. This creates and operates under its’ own vacuum within the NexGen rotor stator chamber. https://hockmeyer.com/products/nexgen-vacuum-rotor-stator/
The unique and highly purpose focused stator design was developed in our research laboratory and is covered by patent 11,110,409. Enabling the dispersion of pigments produced to reach particle size well below 200 nanometers requires substantial time, around 12 hours. However, the particles are now in the dispersion range for a NexGen Vacuum Media Mill to take them to the finish line at or below 10 nanometers.
Comparable results can be obtained by cascade media milling, starting with larger media (.8 to 1.0), and working down multiple bead diameters. Using this approach, the cost of getting to D50 below 200 nm particle size is initially greater when considering the capital cost for the number of media mills required to accommodate the number of bead size changes to get there. Nonetheless, a premix is still preferable for the slurry entering the mill(s). The finer the premix, the faster the media mill can reach the goal line.
In this ongoing pursuit of dispersion improvement, the next post will address how to determine the most productive time in a NexGen Vacuum Rotor Stator with the most productive time in a NexGen Vacuum Mill. https://hockmeyer.com/products/nexgen-recirculation-mill/ When to use one or the other or both.

Vacuum dispersion minus an external vacuum holding tank
The significance of vacuum dispersion has been discussed in previous blogs, focused on improvements enabled by the NexGen Rotor Stator (HNG-RS). This post describes the difference between using a rotor stator pump mixer compared to the HNG-RS.
Vacuum created by pump-type mixers is only on the input side of the device and is typically filled with air. A separate vacuum holding/recirculation tank must be positioned on the output side. In that case, only low vacuum can be pulled because higher vacuum creates cavitation within the rotor-stator, generating heat, noise, and micronizing air bubbles. Removing tiny air bubbles in the vacuum/recirculation tank is challenging, inefficient, adding additional cost and time to the process.
The HNG-RS does not require a separate vacuum holding tank. The air bubbles burst because they have become enlarged within the mill vacuum chamber and are fragile. When returned to normal atmospheric pressure, they burst and become part of the atmosphere they came from. Any clean production holding tank will suffice.
Contact Hockmeyer Today
Hockmeyer Equipment Corporation is here to help you achieve your production goals with innovative, customized solutions. For inquiries or to learn more about how our rotor stator systems can enhance your operations, visit our Contact Page and connect with our team of experts.

